MATH AND NATURE



In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point.

MOON FORMING PARTS OF CIRCLE CALLED SEGMENTS
Elliptical Orbits
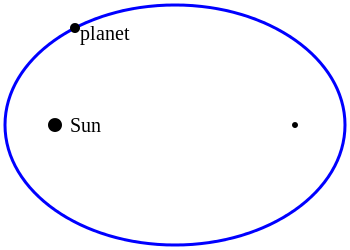
An ellipse is a squashed circle with two focus points or foci, planets orbit in an elliptical path. On the diagram to the right the Sun sits at one of the foci, and the other foci is empty (black dot), the planet orbits around the ellipse.
The amount the ellipse is squashed, or the 'flattening' is called the eccentricity. The more squashed, the higher the eccentricity. A circle has an eccentricity of 0, the more squashed an ellipse becomes more flattened the eccentricity approaches 1. So, all ellipses have eccentricities lying between 0 and 1.
The orbits of all the planets are ellipses, but for most the eccentricities are so small that they look circular. Mercury, along with the Dwarf Planets Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, and Eris, have more eccentric orbits that look more elliptical.

CIRCULAR HELIX
A circular helix, (i.e. one with constant radius) has constant band curvature and constant torsion. A curve is called a general helix or cylindrical helix if its tangent makes a constant angle with a fixed line in space. A curve is a general helix if and only if the ratio of curvature to torsion is constant.



HEXAGONAL WAX


SIX POINT CRYSTAL

FRACTION IN AN ORANGE


LEVEL CURVES IN A TREE

CIRCLE BAND IN SOLAR ECLIPSE

A logarithmic spiral, equiangular spiral, or growth spiral is a self-similar spiral curve that often appears in nature.

SYMMETRY

PENTAGONAL WEB


Comments
Post a Comment